- Product
-
Solution
-
By Industry
Cybersecurity solutions tailored to your industry’s needs.
-
- Resources
-
Books
Our ultimate guides and playbooks
Solution Briefs
Overview of PureDome’s functionality
-
Quizzes
Assess your cybersecurity readiness
Case Studies
PureDome customer success stories
Newsletter
Subscribe to the PureDome newsletter
-
- About Us
- Partner
- Pricing
- Download
Site to Site VPN Security Best Practices
-
Aiman Ikram
-
13 Jun 2024
- 4 min read


In 2024, businesses often have multiple offices or remote teams that need to stay connected. A site-to-site VPN is like a secure tunnel that links different locations, allowing employees to share data safely and work together as if they were in the same office. In this blog, we'll look at why a business might need a site-to-site VPN and how to keep it secure.
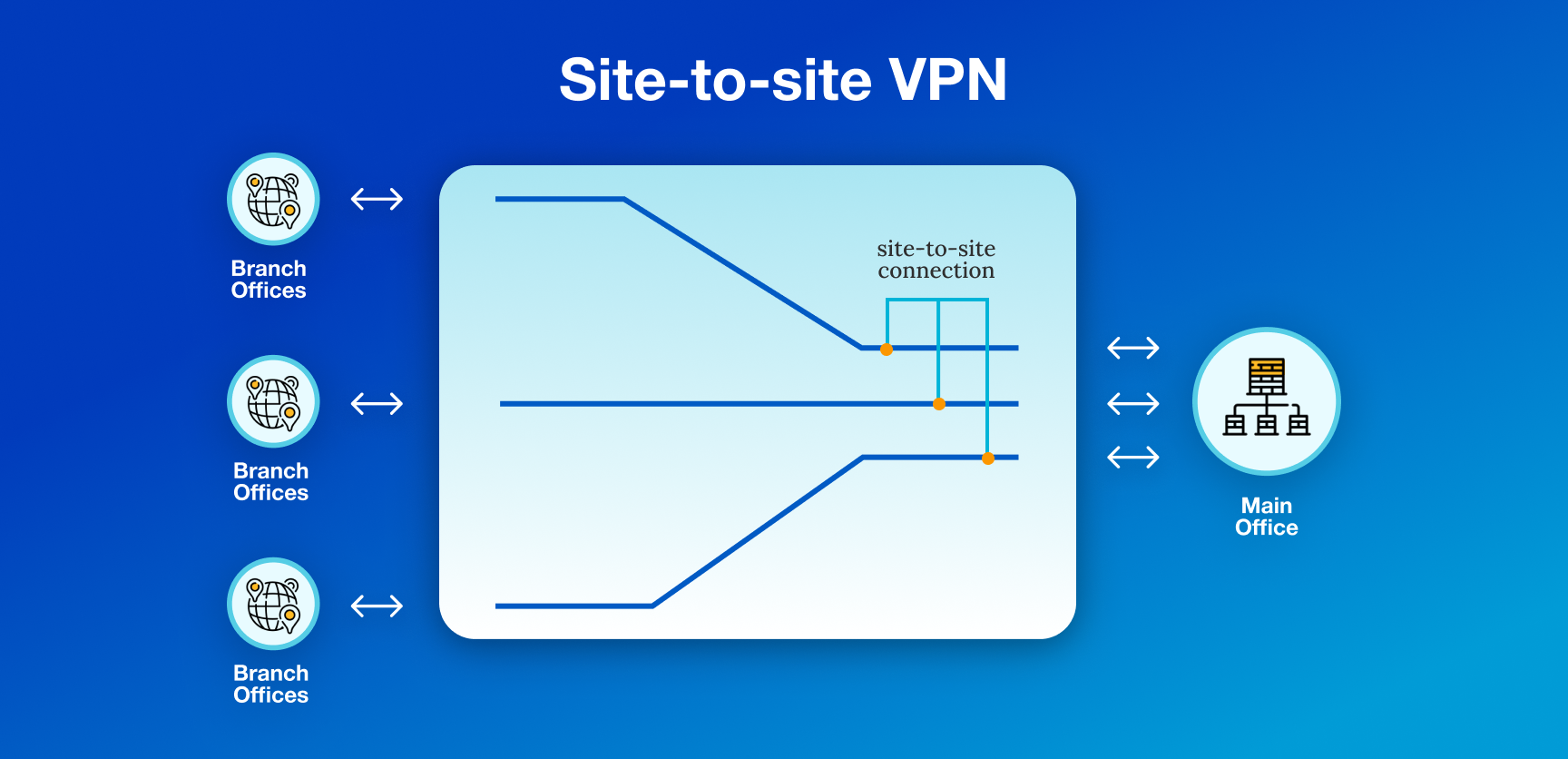
What is a Site to Site VPN
A site-to-site VPN is a secure connection that links two or more different locations, like offices or branches of a company, over the internet. It's like creating a private, encrypted tunnel between these sites, allowing them to share data and resources safely. This helps employees at different locations work together easily and securely, as if they were all in the same office.
What are the best practices for securing a site-to-site VPN?
Encryption: Use strong encryption standards like AES-256 to encrypt the data traveling through the VPN tunnel. This ensures that even if the data is intercepted, it cannot be read without the encryption key. Encryption protects sensitive information from being accessed by unauthorized parties, maintaining the confidentiality and integrity of your data.
Strong passwords: Use complex passwords that combine upper and lower case letters, numbers, and special characters. Avoid using easily guessable passwords. Strong passwords are harder to crack, reducing the likelihood of unauthorized access to the VPN.
Regular updates: Regularly update all VPN-related software and firmware, including VPN clients, servers, and associated networking hardware. Apply patches promptly. Updates often contain security patches for vulnerabilities that could be exploited by attackers. Keeping systems updated reduces the risk of these vulnerabilities being exploited.
Firewalls: Use firewalls to create a barrier between your internal network and external threats. Configure firewalls to inspect and filter traffic entering and leaving the network. Firewalls help prevent unauthorized access and can block malicious traffic, providing an additional layer of security.
Authentication: Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) which requires users to provide two or more verification factors to gain access. This could include something they know (password), something they have (security token), and something they are (biometric verification). MFA adds an extra layer of security by ensuring that even if one authentication factor is compromised, unauthorized users still cannot access the VPN without the additional verification.
Monitoring: Use network monitoring tools to continuously monitor VPN traffic and logs. Look for unusual patterns that might indicate a security issue, such as unexpected login attempts or data transfers. Continuous monitoring helps in the early detection of potential security breaches, allowing for prompt response and mitigation.
Access control: Implement strict access controls to limit VPN access based on roles and responsibilities. Use principles like least privilege, ensuring users only have access to the resources they need. Limiting access minimizes the potential damage that could be caused by compromised accounts or malicious insiders.
VPN policies: Develop comprehensive VPN usage policies that outline acceptable use, security requirements, and user responsibilities. Ensure employees are trained and aware of these policies. Clear policies help ensure consistent and secure use of the VPN across the organization, reducing the risk of human error.
Auditing: Regularly audit VPN logs, configurations, and access records. Conduct periodic security assessments and vulnerability scans. Auditing helps identify and rectify security weaknesses, ensuring compliance with security standards and regulations.
Backup: Maintain regular backups of critical data and VPN configurations. Store backups securely, and ensure they are tested and updated regularly. Backups ensure that you can quickly restore operations and data integrity in case of a security breach or system failure, minimizing downtime and data loss.
How do you ensure security in a site-to-site VPN setup?
To ensure security in a site-to-site VPN setup, start by using strong encryption to protect data traveling between sites. Make sure to use complex, unique passwords and regularly update all VPN-related software and hardware to prevent vulnerabilities. Implement firewalls to filter traffic and use multi-factor authentication to verify users.
Continuously monitor VPN traffic for any unusual activity and restrict access based on roles, ensuring only those who need it can use the VPN. Develop clear usage policies and regularly audit your setup to identify and fix any weaknesses. Finally, maintain regular backups of critical data and configurations to quickly recover from any incidents.
What are the key components of a secure site-to-site VPN?
VPN Gateway: Acts as the entry point for VPN connections and manages traffic between sites.
Tunneling Protocol: Establishes secure connections and encrypts data during transmission.
Authentication Mechanism: Verifies the identity of users and devices accessing the VPN.
Routing: Directs traffic between connected sites efficiently and securely.
Network Address Translation (NAT): Translates IP addresses to ensure compatibility and security across different networks.
Quality of Service (QoS): Prioritizes VPN traffic to maintain performance and reliability.
Redundancy: Provides backup connections or failover mechanisms to ensure continuous operation.
Logging and Auditing: Tracks VPN activity for monitoring, troubleshooting, and security analysis.
Compliance and Standards: Adheres to industry regulations and best practices for data protection and security.
How to manage and monitor site-to-site VPN security?
Managing and monitoring site-to-site VPN security involves several key steps. Start by establishing clear policies outlining who has access to the VPN and under what conditions. Regularly update VPN software and hardware to patch vulnerabilities and ensure they meet security standards.
Use monitoring tools to keep an eye on VPN traffic and logs for any unusual activity that could indicate a breach. Implement multi-factor authentication to verify user identities securely. Conduct regular audits of VPN configurations and access logs to identify and address potential security weaknesses.
Finally, maintain backups of critical data and configurations to quickly recover in case of a security incident. By following these practices, businesses can effectively manage and monitor site-to-site VPN security to protect sensitive information and maintain operational integrity.
How PureDome helps
PureDome enhances site-to-site VPN security by providing robust security solutions tailored to protect your network. It offers advanced encryption protocols, real-time monitoring, and automated threat detection to safeguard data transmitted between sites.
PureDome's intuitive management interface simplifies VPN configuration and ensures compliance with security policies. With PureDome, businesses can effectively manage and mitigate security risks, ensuring reliable and secure communication across their network infrastructure.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a site-to-site VPN?
A site-to-site VPN securely connects multiple locations, like offices, over the internet, allowing them to share data and resources.
How do you ensure security in a site-to-site VPN setup?
Ensure security through encryption, strong passwords, regular updates, firewalls, multi-factor authentication, monitoring, access controls, policies, auditing, and backups.
What are key components of a secure site-to-site VPN?
Key components include VPN gateways, tunneling protocols, authentication mechanisms, routing, NAT, QoS, redundancy, logging, and compliance with standards.