- Product
-
Solution
-
By Industry
Cybersecurity solutions tailored to your industry’s needs.
-
- Resources
-
Books
Our ultimate guides and playbooks
Solution Briefs
Overview of PureDome’s functionality
-
Quizzes
Assess your cybersecurity readiness
Case Studies
PureDome customer success stories
Newsletter
Subscribe to the PureDome newsletter
-
- About Us
- Partner
- Pricing
- Download
Navigating Remote Working Security Risks in 2024
-
Aiman Ikram
-
22 Apr 2024
- 5 min read

-1.jpg?width=706&height=440&name=Thumbnail%20(4)-1.jpg)
Remote work isn't merely a trendy benefit provided by a handful of innovative companies—it's become the standard. According to USA Today, more than half of office workers now prefer working from home at least three days a week. It's no surprise, considering the perks like flexibility and better balance between work and life. But, there's a catch – remote work also brings along some serious security concerns for CISOs and cyber security professionals.
Researchers have repeatedly pointed out the increased cybersecurity risks associated with remote work. Gitnux reports that a staggering 67% of companies have experienced cyberattacks since transitioning to remote work. While this might sound alarming, it's reassuring to know that 94% of those affected by cyber attacks have seen improvements in their cybersecurity with the adoption of cloud technology.
This article dives into the top cybersecurity risks of remote work in 2024 and offers practical steps to create a secure remote work setup.
Why Does Remote Work Increase Cyber Security Risk: Key Insights
HP Inc highlighted the cyber risks linked with remote work in its HP Wolf Security Blurred Lines & Blindspots Report 2021. Here are some key insights from the study:
- 70% remote workers use work devices for personal activities
- Cyber attacks went up by 238% during the pandemic
- 54% of ITDMs witnessed rise in phishing; 56% saw more web browser infections
The insights above show that working from home gives rise to new cyberthreats that are not seen in traditional office environments.
What are the Key Cyber Security Risks of Working Remotely?
CISOs and CSOs are justified in their rising concerns regarding remote work security. So, what risks exactly does remote working create? Let us explore the top 6 cyber security risks that remote workers are facing this year:
1. Endpoint Vulnerabilities
When working from home, employees are facing a whole new set of challenges compared to the office. There's a higher risk of cyberattacks because they’re using our own devices and networks, which might not be as secure.
Cybercriminals see this as an opportunity to strike with malware and ransomware. Plus, the security measures at home aren't always as strict as they are in the office, making them more vulnerable to breaches. And if they’re not following the best security practices, things can get even riskier.
2. Unsecured Wi-Fi Networks
Using unsecured Wi-Fi networks is risky. Cybercriminals can intercept data on these networks. This includes sensitive information like login credentials and financial data. Hackers might even create fake Wi-Fi networks called "evil twins" to trick users into connecting, posing a serious threat to remote workers' security. This threat worries remote workers so much that even the US Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) warned about it last year.
3. Insider Threats and Data Theft
Remote workers often feel less monitored, making it easier to bend the rules without anyone noticing. Feeling disconnected from the company might push them towards risky behavior too. Sometimes, they meddle with security protocols either by accident or on purpose, which can lead to data leaks. And when work and personal life blend together, it's easier for slip-ups to happen. This is true especially if they're using their own devices or unprotected networks.
4. Inadequate Access Controls
In remote work, insufficient access controls are a big cybersecurity risk. Employees might access sensitive data accidentally, increasing the chance of breaches. It's hard to enforce consistent security rules across different devices and places. This makes it easier for criminals to exploit weaknesses. They can access corporate networks without permission, leading to legal trouble for companies.
5. Slow Incident Response Time
Responding to incidents can be slow because of communication problems and technical issues. These delays make security problems worse. This is because they cause data loss and disrupt business. IBM found that companies with remote workers took 58 extra days, on average, to deal with breaches compared to those without remote teams.
6. Expanded Attack Surface
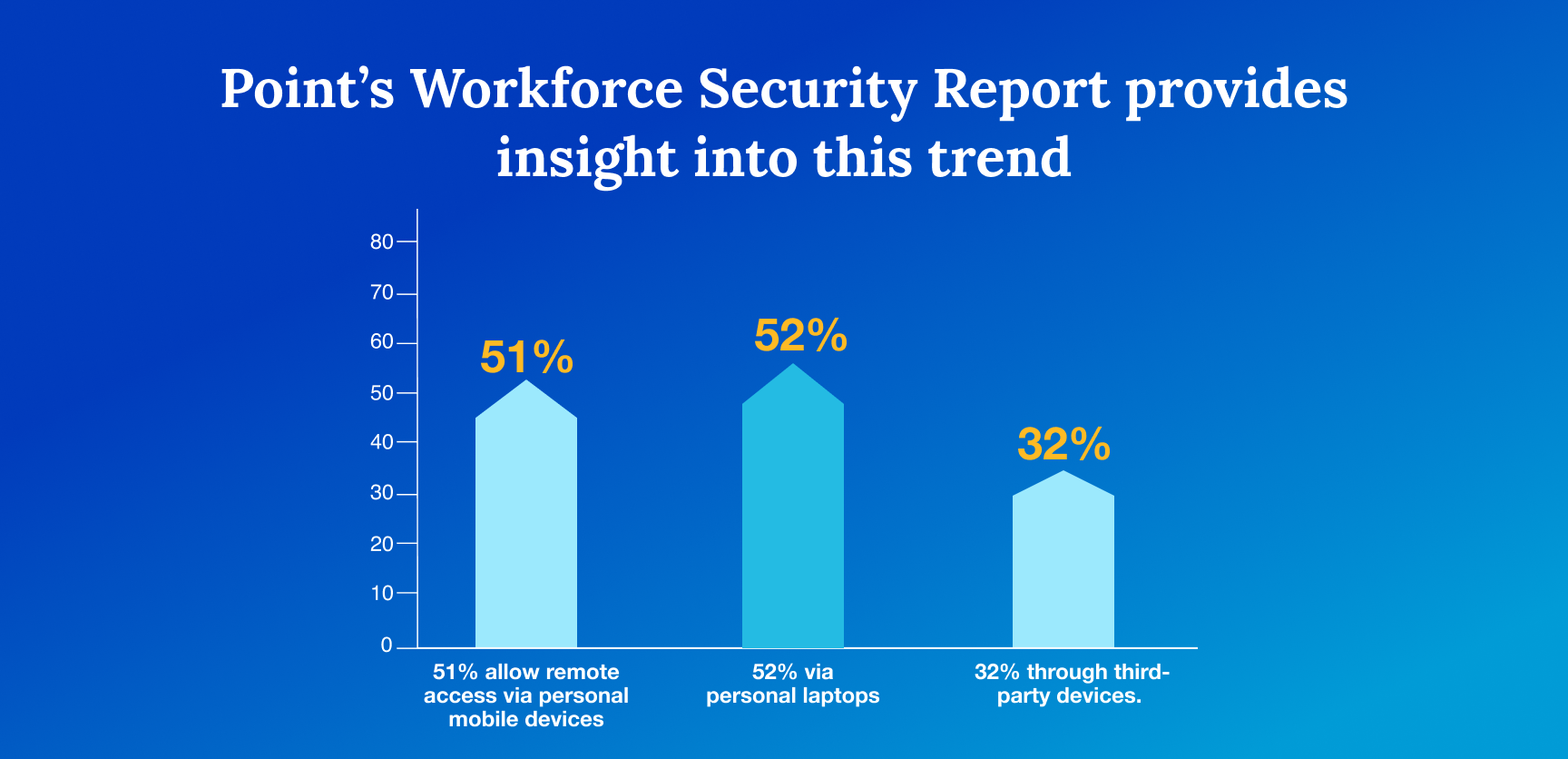
Many organizations permit employees to access corporate applications using personal devices. Check Point’s Workforce Security Report provides insight into this trend: 51% allow remote access via personal mobile devices, 52% via personal laptops, and 32% through third-party devices.
Given the diverse array of locations and devices employees use, there is more room for vulnerabilities. Consequently, there are heightened concerns regarding data breaches, malware, and unauthorized access.
Remote Work Security Best Practices
Enhancing security in company networks involves multiple steps. First-off, it includes upgrading systems and implementing solutions to reduce security risks. There is also a need to boost efficiency across the infrastructure and ensure the protection of important data.
We've got some top tips lined up to help you make remote work safer.
Zero Trust Network Access Implementation
You must be aware of Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA). It is an important principle in cybersecurity in 2024. It is especially useful in remote work. Due to its benefits in terms of remote work security, the global Zero Trust security market amounted to over 31.6 billion U.S. dollars in 2023 and is forecast to increase to 133 billion U.S. dollars by 2032. It assumes that no user or device should be trusted by default, regardless of their location or credentials.
It helps organizations enforce strict access controls based on the principle of least privilege. This ensures that remote workers only have access to the resources they need to perform their job responsibilities.
This mitigates the risk of unauthorized access and lateral movement within the network. ZTNA also has visibility into user activity. It also helps you monitor network traffic. This helps organizations to detect and respond to suspicious behavior in real-time.
Multi-Factor Authentication/Two-Factor Authentication (MFA/2FA)
MFA/2FA, a vital security measure, adds an extra layer of protection to passwords. It needs remote workers to verify their identity. It uses multiple factors like passwords, biometrics, or one-time codes. This lowers the risk of unauthorized access to company systems and data. MFA/2FA helps prevent phishing, credential theft, and account compromise by allowing only authorized users to access sensitive information.
Endpoint Protection Solutions
Endpoint security is crucial. It is important to lock down those endpoints: laptops, mobile gadgets, and home computers. Making sure they're armed with the latest internet security software is your frontline defense against unauthorized access and possible security breaches that could spring from vulnerable personal devices.
Encrypt Data in Transit and at Rest
Encryption is key to keeping your data safe when employees are on unsecured networks or using personal devices. It locks down data while it's being transferred, making sure cyber attackers don’t get their hands on it. And when data is at rest, encryption still has your back, protecting sensitive info stored on remote devices or in the cloud. It's a solid defense against data theft and compliance issues.
VPN Usage (Virtual Private Network)
Business VPNs secure remote connections and data on unsecured networks. They create encrypted tunnels between devices and corporate networks. VPNs ensure data confidentiality. Employees often connect from public Wi-Fi, so VPNs reduce interception risks. They prevent eavesdropping and unauthorized access. They also enable access control enforcement and user activity monitoring.
Prioritize Cybersecurity Training
30% of remote workers lack consistent training from employers. Data Basix shows 44% have no cyber security training for remote work. This is a real wake-up call and shows that we need a change. Remote workers need easy access to security policies and training materials. We should keep them informed about threats and best practices.
How Does PureDome Help You Stay Secure When Working Remotely?
PureDome offers security solutions for remote work safety. With Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA), PureDome's cybersecurity system carefully checks access requests. It cuts down on entry without authorization. It also provides extra security features like Site-to-site VPN, Two-Factor Authentication (MFA), Device Posture Check, and Identity and Access Management (IAM) solutions. Using PureDome's solutions helps companies keep their remote work environments secure.
Final Verdict
It's crucial for organizations to recognize the security risks that come with remote work. By embracing best practices and utilizing advanced security solutions like PureDome, they can tackle these challenges head-on. This ensures their data and operations stay protected not just in 2024, but well into the future.
.png?width=1728&height=836&name=Blog%202%20(1).png)