- Product
-
Solution
-
By Industry
Cybersecurity solutions tailored to your industry’s needs.
-
- Resources
-
Books
Our ultimate guides and playbooks
Solution Briefs
Overview of PureDome’s functionality
-
Quizzes
Assess your cybersecurity readiness
Case Studies
PureDome customer success stories
Newsletter
Subscribe to the PureDome newsletter
-
- About Us
- Partner
- Pricing
- Download
The Role of Data Encryption in Healthcare
-
Aiman Ikram
-
30 Jan 2024
- 7 min read

-1.webp?width=864&height=418&name=cover%201%20(1)-1.webp)
Secure remote access is essential for modern workplaces. The rise of the Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) culture in the remote work era has led to a concurrent increase in security threats.
According to Helpnet Security's survey, 63% of respondents recognized data leakage as their primary concern with the BYOD culture, with an additional 57% expressing worries over the potential risks associated with downloading unsafe applications or content. Issues like malware exposure from home networks, the absence of critical security updates on mobile devices, or the lack of encryption can all hinder network access. This is precisely where the significance of the Device Posture Check becomes evident.
Our infographic details how coupling your cybersecurity solutions with device posture checks is essential for ensuring secure remote access for your business operations.
Overview:
According to IBM's Cost of a Data Breach Report 2023, the healthcare industry has consistently had the highest data breach costs for 13 consecutive years. To proactively defend against these threats, strong cybersecurity measures, including encryption, are crucial. It is vital to encrypt all digital records, communications, and endpoint devices to ensure that even if hackers gain access to the data, they are unable to comprehend it. Encryption is not only important for security but also required by most cybersecurity regulatory compliance such as HIPAA, GDPR and PCI-DSS. With the advancement of quantum computing posing a great threat to current encryption algorithms, it’s important to understand how clinics and medical institutions can protect their data and systems against such advanced forms of cyberattacks.
Importance of Cybersecurity in Healthcare:
The growth in digitalization has made the security of digital assets a critical issue, particularly in industries like Healthcare. In the current landscape, the amount of cyberthreats on electronic Protected Health Information has considerably amplified due to its value as it can be sold for high prices in illegal markets. In such circumstances, cybersecurity becomes of utmost importance. A cyberattack can result in financial losses, data loss, reputation damage, and in the case of healthcare services,it can cause the hospital equipment to fail or alter the patient records which can even have severe effects on a patient's health.
What is Encryption?
-1.webp?width=1728&height=836&name=cover%202%20(1)-1.webp)
Encryption is the process of converting sensitive information into an incomprehensible format to prevent unauthorized access. Even if a hacker is able to obtain the encrypted data, they will be unable to understand it. This is achieved using complex encryption algorithms and cryptographic keys, which are used to encrypt and decrypt the message. Encryption serves not only to hide sensitive information but also to ensure message integrity, protecting against any unauthorized reading or manipulation of stolen data, typically involving two categories: data in transit or data at rest.
Types of Encryption:
While numerous encryption algorithms exist, they are generally classified as either symmetric or asymmetric cryptographic algorithms. In symmetric encryption, the sender and receiver share identical keys, employed for both encryption and decryption. Hospitals favor using symmetric encryption like AES for storing private data and internal communications. In contrast, asymmetric encryption involves two distinct keys: a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption. Asymmetric encryption algorithms like RSA are utilized by healthcare institutes for external communications, key exchange and authentication. End to End encryption (E2EE) is a popular type of encryption due to its level of privacy and confidentiality, this is because in E2EE even the third party platforms don’t have any access to the data being transferred from one endpoint to another.
Challenges in Healthcare:
The healthcare sector safeguards highly sensitive data, including patient records, billing information, and medical research, requiring robust protective measures. A breach of ePHI(electronic Protected Health Information) can have severe consequences as it can damage reputation and also affect the consumers as the records can be sold on dark web and be used for financial gains or impersonation.
Beyond the financial implications, any disruption in workflow resulting from a cyberattack can have immediate repercussions on patient health. One example of this is when ransomware attacked a hospital in Duesseldorf, Germany due to which the IT systems at the hospital failed. A woman who needed urgent treatment passed away as she was required to move to another city due to the system's failure. This incident underscores the importance of reinforcing cybersecurity protocols to uphold the integrity of healthcare systems.
Regulatory Requirements and Compliance:
-1.webp?width=1728&height=1000&name=cover%203%20(1)-1.webp)
Healthcare organizations must adhere to strict compliance regulations, particularly in the realm of cybersecurity and encryption. The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) is a U.S. congressional act safeguarding medical records and personal health information. HIPAA mandates the encryption of all Electronic Medical Records, whether stored on a staff computer or transmitted via email. Furthermore, the Quality System Regulation stipulates the necessity for robust encryption to ensure the safety of Medical Devices. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) recognizes health-related data as a special category, demanding robust encryption measures. This highlights the pivotal role of encryption in regulatory compliance.
Implementing Data Encryption in Healthcare Systems:
To implement a robust data encryption system, you should begin with classifying the data according to its level of sensitivity. Align your encryption policies with the regulatory requirements and organizational goals. Specify the encryption algorithms to be used for data in transit and data at rest and choose encryption solutions that can be integrated into the healthcare systems seamlessly. When choosing encryption solutions, it is important to consider how scalable the solutions are and how they will impact the performance of the systems.
Overcoming Challenges in Data Encryption Adoption:
Perceived as a complex technology, encryption may face resistance from healthcare staff; however, overcoming this challenge is achievable through targeted training sessions on the usage and benefits of encryption. Considering cost as a significant factor in implementing security measures like encryption, exploring cost-effective and economical solutions is essential. The integration of encryption can disrupt organizational operations, and to mitigate this, a phased approach can be adopted to minimize disturbance and facilitate a smoother transition.
Best Practices:
Electronic Health Records:
Electronic Health Records, commonly known as EHRs, represent a digitized version of a patient's medical history. They serve to enhance data availability for authorized users and are space-efficient. However, the electronic format poses a cybersecurity risk, as hackers may attempt to steal sensitive data, such as patient records, for malicious purposes. Due to which it is crucial to encrypt these records, preventing hackers from exploiting the data even if they manage to gain unauthorized access.
Data in Transit:
Healthcare professionals and staff regularly exchange vital patient information and confidential organizational data through various digital channels. Consequently, it is paramount to prioritize the security of these communication avenues. A highly effective approach is to employ encryption for these channels, mitigating the risk of unauthorized access and safeguarding the privacy of sensitive information. It is recommended to secure the communication channels using security protocols like Transport Layer Security (TLS). Opting for encrypted emails and utilizing secure messaging platforms emerges as some of the most robust strategies for fostering a secure and confidential communication environment in the healthcare sector.
Endpoint Device Encryption:
Numerous devices, including mobile phones, laptops, and computers, are integral to the healthcare network for storing critical medical data and facilitating communication. However, these devices are susceptible to hacking and cyberattacks, emphasizing the need for robust protective measures. Enabling endpoint device encryption is highly recommended. This ensures that in the event of theft or loss, unauthorized individuals cannot access or manipulate the data stored on the device.
Key Management:
Keys constitute the most crucial component of an encryption algorithm since information can only be decrypted using these keys. Therefore, it is essential to secure these keys to ensure the protection of encrypted data. The keys should be handled with the utmost care throughout their entire lifespan. Additionally, implementing Periodic Key Rotation, wherein encryption keys are changed at regular intervals, is also highly significant. This practice ensures that even if a key is compromised, it can only be utilized for a limited period.
Data in Transit:
Healthcare professionals and staff regularly exchange vital patient information and confidential organizational data through various digital channels. Consequently, it is paramount to prioritize the security of these communication avenues. A highly effective approach is to employ encryption for these channels, mitigating the risk of unauthorized access and safeguarding the privacy of sensitive information. It is recommended to secure the communication channels using security protocols like Transport Layer Security (TLS). Opting for encrypted emails and utilizing secure messaging platforms emerges as some of the most robust strategies for fostering a secure and confidential communication environment in the healthcare sector.
Regular Audits, Updates and Reviews:
It is important to assess the strength of your security measures to ensure and maintain a strong security posture. For this purpose, regular audits come in handy as they allow you to test the robustness of your encryption protocols and identify vulnerabilities. Watching out for emerging threats is crucial as you need to have your solutions updated with the latest security patches. Cybersecurity is one of the most evolving landscapes due to which it is important to review your encryption policies and adapt to the changes.
Data at Rest:
Healthcare organizations store data in various forms ranging from archives to cloud storage solutions. The data stored in databases, servers and other storage systems should be encrypted as this will minimize the risk of unauthorized access in the event of a security break. Even when storing data on the cloud, it is important to ensure that it is encrypted so that even if the cloud service is attacked, it does not reveal any confidential information.
Human Factor: .webp?width=1728&height=836&name=cover%204%20(1).webp)
The human factor contributes to nearly 95% of all security incidents. Therefore, even with robust encryption measures in place, it is crucial to educate healthcare staff on the significance of data encryption. Staff members need to understand their pivotal role in protecting patient and organizational data. Regular training programs should be conducted to ensure adherence to the organization’s security protocols. These programs should encompass the basics of encryption, its importance, and regulatory compliance. Such initiatives not only enhance the security of critical data but also bolster the overall security posture of the organization.
Other Security Measures:
While encryption stands as a robust security measure, its effectiveness is heightened when integrated with other cybersecurity measures. Healthcare facilities should employ Firewalls, Antiviruses, and Intrusion Detection Systems to fortify defenses against cyberattacks. Firewalls safeguard against external intrusions, antivirus programs combat malware, and intrusion detection systems monitor network activities for any anomalies, providing timely threat alerts. Additionally, it is crucial to develop a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy to ensure compliance and maintain a strong security posture.
Real Life Case Studies:
Several real-life case studies exemplify the practical efficacy of encryption in risk mitigation and safeguarding patient data. The Mayo Clinic, a prominent healthcare center in America, is a notable example. It employs encryption to secure sensitive medical data during storage and transmission. The Mayo Clinic has formed a strategic partnership with TripleBlind to validate the interoperability of encrypted algorithms on encrypted data. Additionally, they collaborate on training new algorithms using encrypted data, showcasing a commitment to advancing secure practices in healthcare through innovative encryption applications.
Future Trends: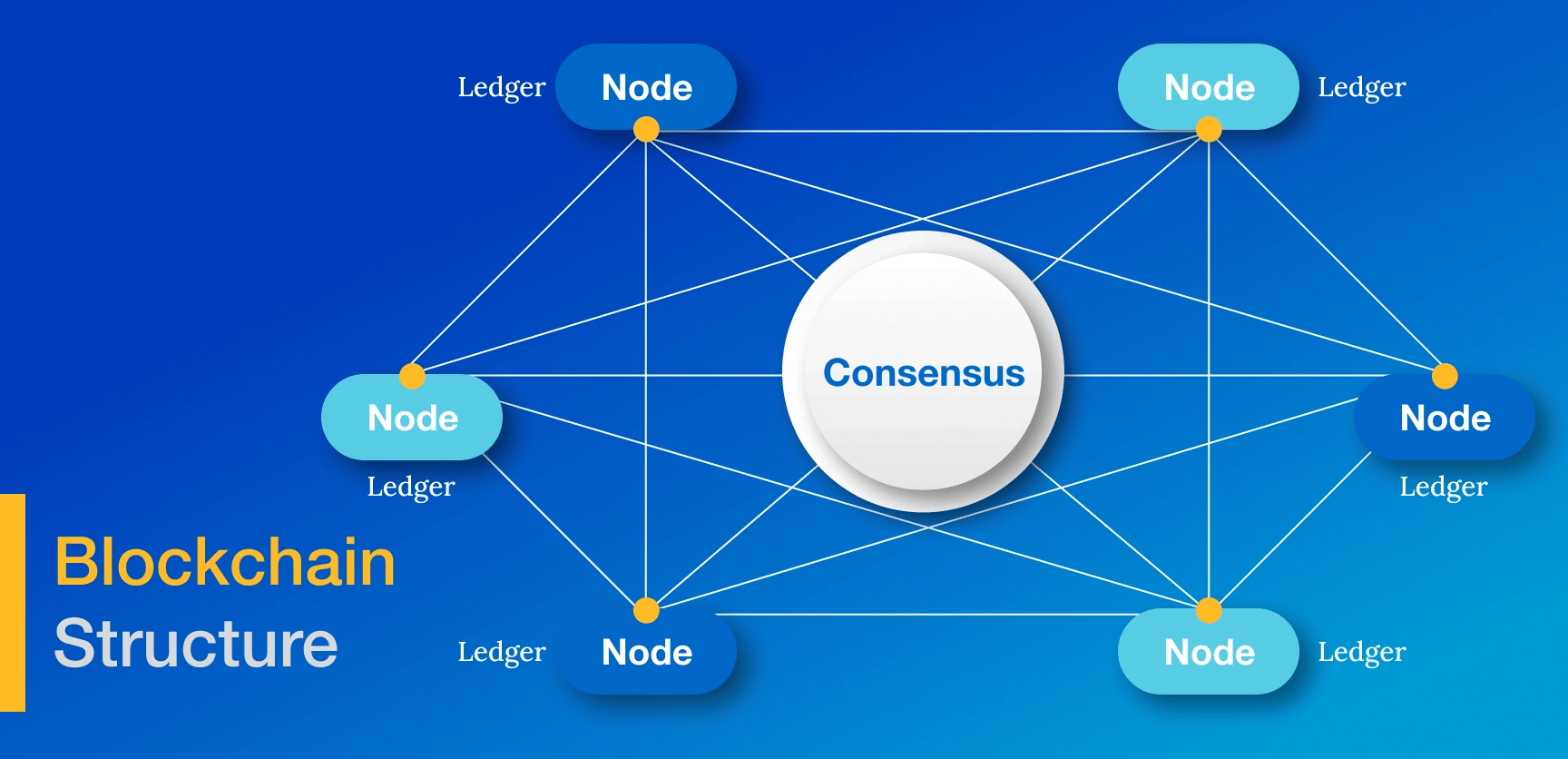
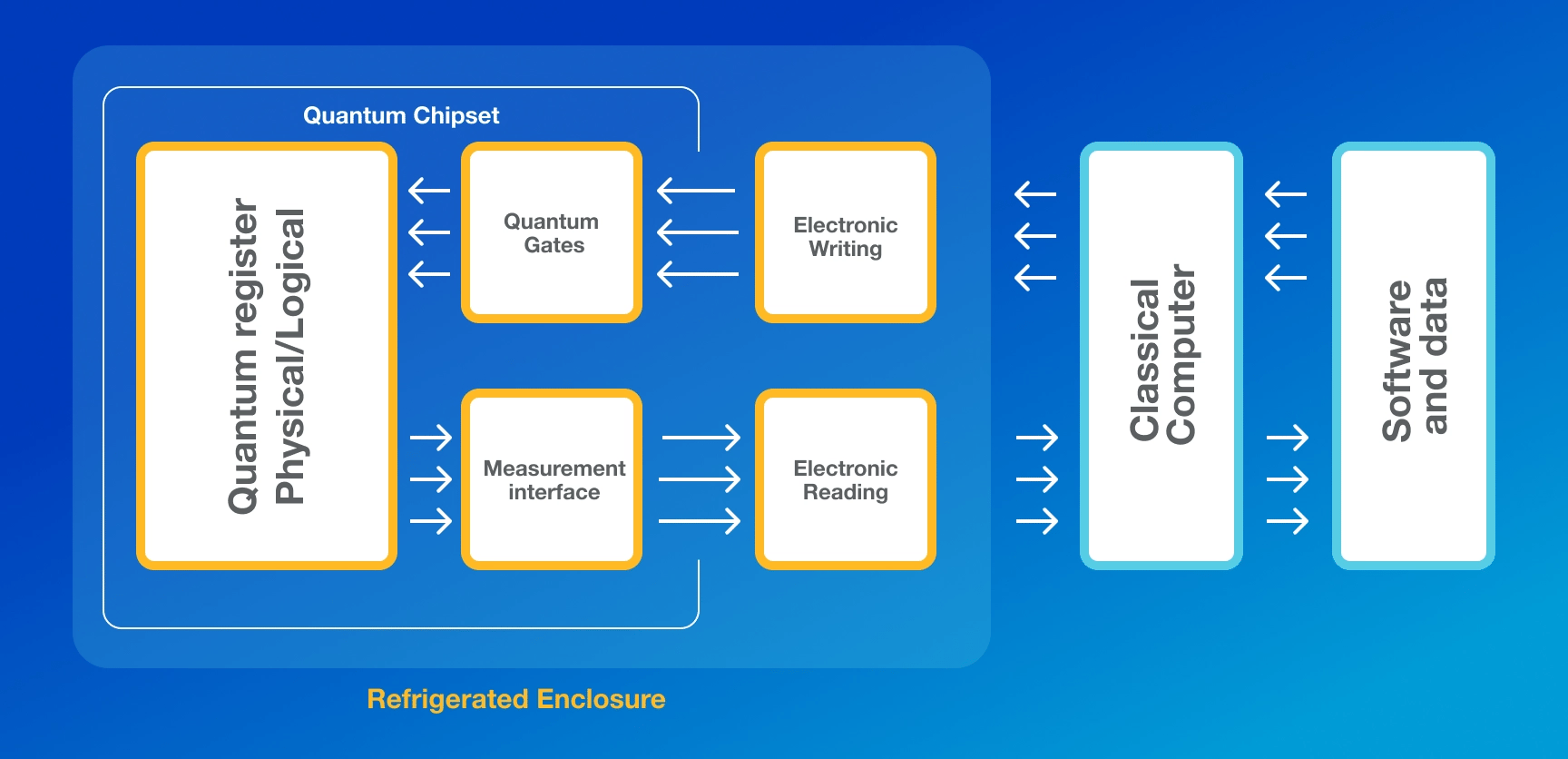
As technology advances, the landscape of healthcare data encryption is rapidly evolving. Emerging technologies, such as Blockchain and Quantum Computing, are poised to shape the future of healthcare data protection. Blockchain, known for its tamper-resistant nature, can be employed to preserve the integrity of electronic medical records. On the other hand, Quantum Computing poses a significant threat to current encryption algorithms. This is because many cryptographic algorithms depend on keys that can be easily brute-forced by Quantum Computers, given their exceptional processing power.
Conclusion:
To sum up, encryption is the cornerstone for ensuring privacy and integrity of patient information in the healthcare sector. To create a robust security ecosystem, it is important for an organization to follow the cybersecurity best practices. Furthermore, going along with the regulatory requirements is also a must for every Healthcare organization. This will not only improve the organization’s security posture but also increase customers’ trust. As we look into the future, it is crucial to embrace the emerging technologies and use them to their benefit. Spend only 9 minutes to learn how PureDome’s cybersecurity solution can help your business augment secure remote access.
Stay up to date with the latest cybersecurity insights and best practices
Get the latest information, stories, and resources in your inbox. Subscribe for monthly updates.
Securing 1000+ Businesses Across The World