- Product
-
Solution
-
By Industry
Cybersecurity solutions tailored to your industry’s needs.
-
- Resources
-
Books
Our ultimate guides and playbooks
Solution Briefs
Overview of PureDome’s functionality
-
Quizzes
Assess your cybersecurity readiness
Case Studies
PureDome customer success stories
Newsletter
Subscribe to the PureDome newsletter
-
- About Us
- Partner
- Pricing
- Download
10 Key Cybersecurity Threats That Virtual Medical Assistants Face and How to Prevent Them
-
Aiman Ikram
-
30 Jan 2024
- 6 min read


Virtual Assistants are becoming an increasingly important part of the healthcare industry. Research Nester reports that the Virtual Medical Assistants (VMA) Market will grow to USD 33 Billion by the end of 2036, showcasing a growth rate of 35% during the forecast period (2024 - 2036). This acceleration is a result of the better health outcomes and lower medical expenses that VMAs contributed to the industry.
However, the integration of these VMAs into the market is directly related to the increasing vulnerability of the healthcare industry toward cybersecurity concerns and threats. In this blog, we delve into the key cybersecurity threats facing VMAs and explore how implementing secure remote access can serve as a robust defense.
What is the Role of VMAs?
VMAs play a crucial role in modern healthcare, automating tasks like appointment scheduling and prescription refills to enhance operational efficiency. They contribute to improved patient engagement by providing personalized information and fostering communication. VMAs manage vast healthcare data, helping doctors organize it and generate insights to make more informed decisions. With 24/7 accessibility, they offer immediate support, reducing the burden on healthcare providers.
VMAs collect and transmit data in remote patient monitoring, enabling timely interventions and reducing hospital readmissions. Advanced language processing makes interactions user-friendly, catering to a broad demographic. Seamless integration with existing systems ensures interoperability and prevents information silos. The integration of AI-powered VMAs allows for sophisticated data analysis and personalized treatment recommendations, contributing to more precise diagnostics and treatment planning in healthcare delivery, making the VMA market grow at an even higher rate.
Why Are VMAs at a Cybersecurity Risk?
The attributes that make VMAs indispensable also render them susceptible to cybersecurity threats. Moreover, Healthcare is perhaps the main industry that is the focal point of cyberattacks across the world. According to CheckPoint Research, healthcare organizations across the world averaged 1,463 cyberattacks per week in 2022, up 74% compared with 2021. One of the main reasons for this is the nature and amount of data that healthcare records hold. This sensitive data includes valuable information like patient location, insurance IDs, healthcare and medical records, and more.
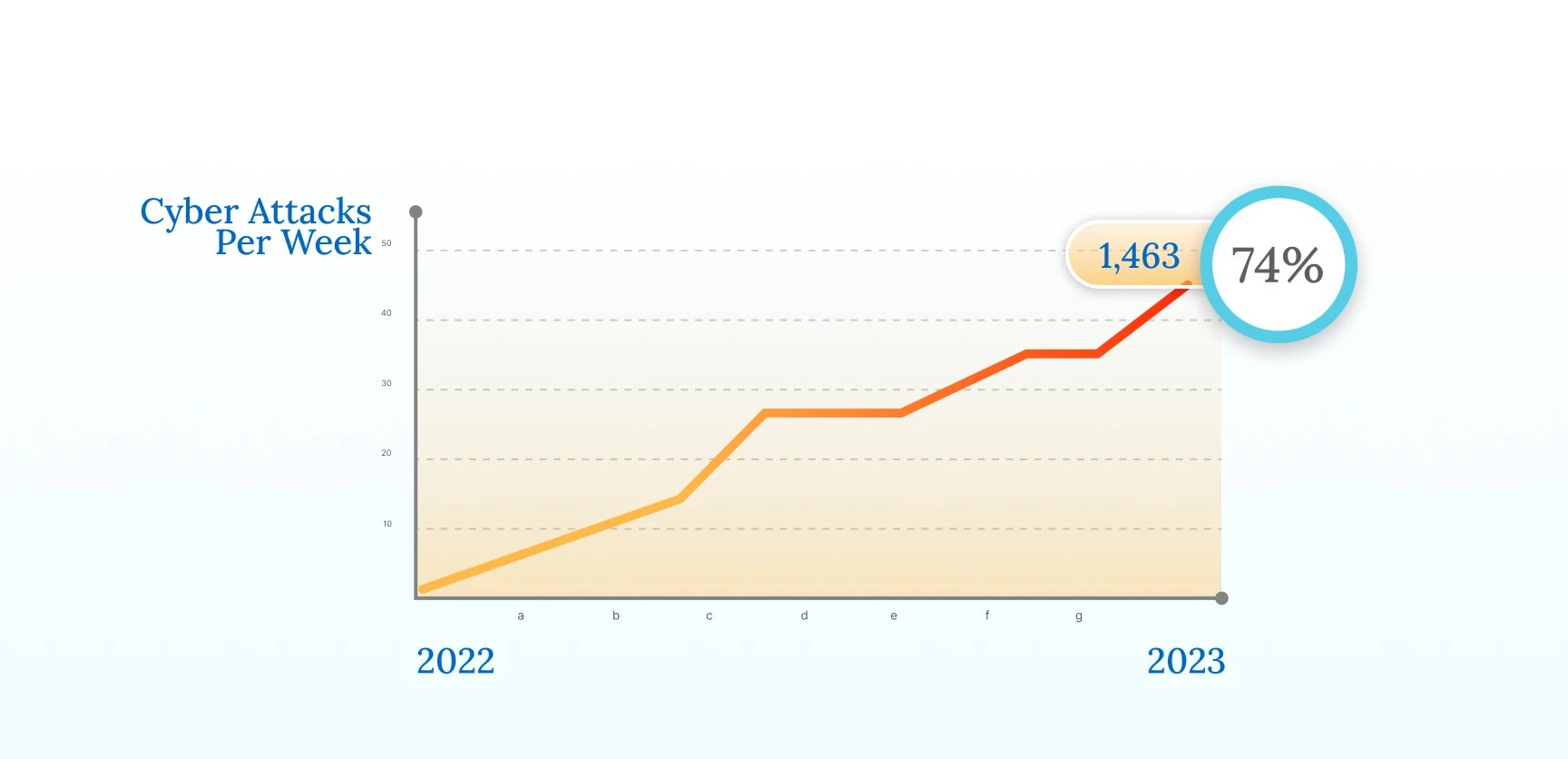
Such data is highly valuable in multiple aspects. For instance, Forbes claims that the value of a health record can be worth as much as $1,000, whereas on the dark web, a credit card number is worth $5, and Social Security numbers are worth only as much as $1.
Since most VMAs work remotely and deal with patients and colleagues from across the world, they offer a larger attack surface. On top of this, with most VMAs being hired hourly, it is common for their devices and connections to miss crucial security posture, making them prime targets for cyberattacks.
What Cyber Threats Do VMAs Face?
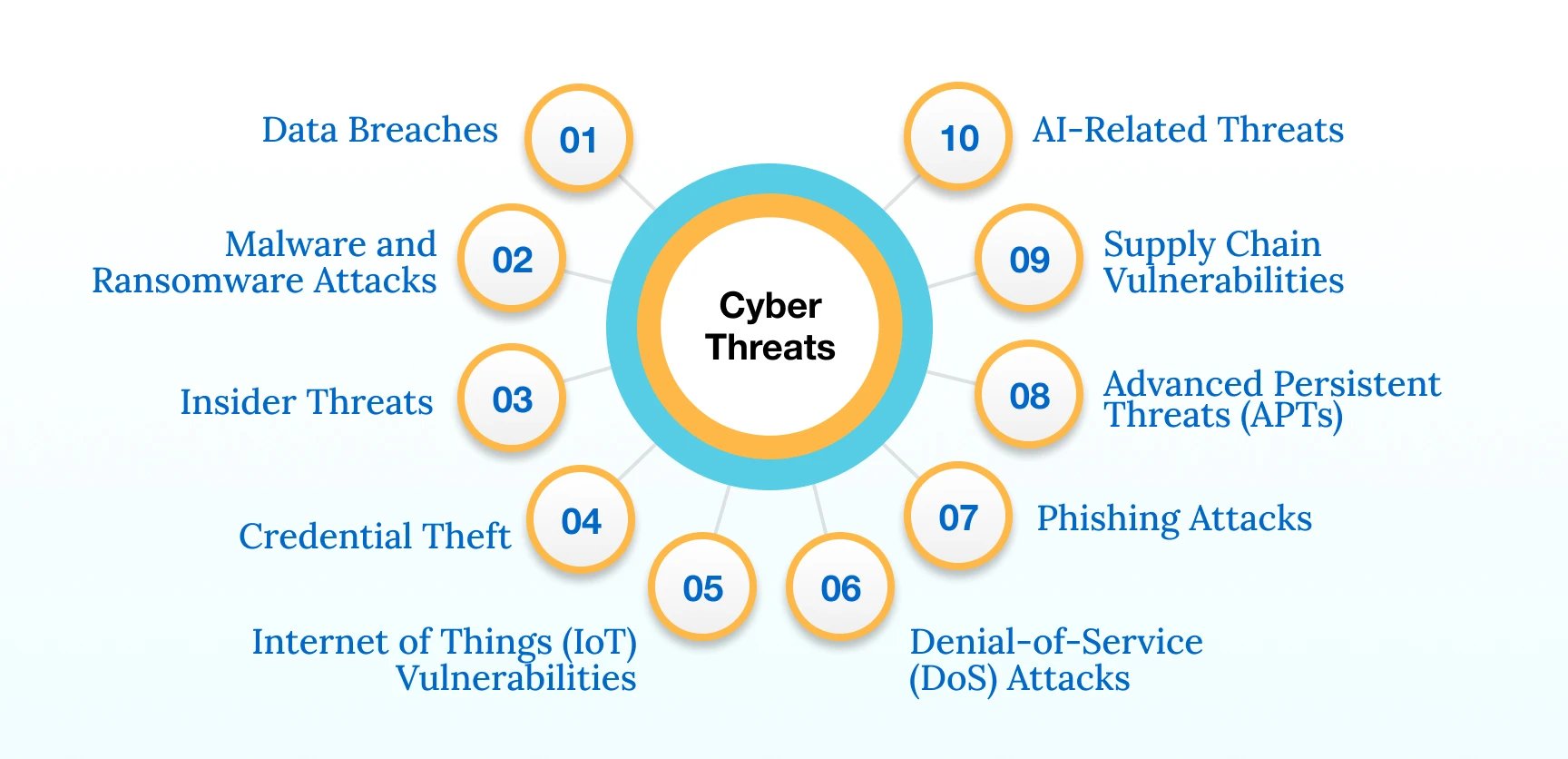
VMAs face a range of cyber threats, including:
- Data Breaches: Cybercriminals exploit vulnerabilities in healthcare systems, gaining unauthorized access to patient databases. This often results from inadequate encryption or weak access controls. Unauthorized access to patient information poses a significant risk, potentially leading to severe consequences for patients, healthcare providers, and the VMA staffing agency.
- Malware and Ransomware Attacks: The healthcare sector is not immune to the increasing frequency and sophistication of malware and ransomware incidents, which can disrupt operations and compromise patient care. Malicious software infiltrates healthcare networks through deceptive emails or compromised websites. Ransomware, once introduced, encrypts data, demanding payment for decryption keys. These are among the major threats that are now being linked to remote workers, such as VMAs and the BYOD culture.
- Insider Threats: The possibility of internal actors misusing their privileges or unintentional breaches highlights the need for stringent security measures within healthcare organizations. VMAs with privileged access may inadvertently compromise security or deliberately misuse their credentials. This can occur through negligence, lack of training, or malicious intent.
- Credential Theft: Unauthorized individuals gaining access to login credentials poses a serious risk, allowing them to exploit sensitive patient data and compromise system integrity. Cybercriminals employ tactics like phishing to trick VMAs into divulging login credentials. Once acquired, these credentials provide unauthorized access to sensitive systems.
- Internet of Things (IoT) Vulnerabilities: The proliferation of IoT devices in healthcare introduces vulnerabilities, providing potential entry points for malicious actors. Weaknesses in the security of connected medical devices, often lacking proper encryption and authentication protocols, create entry points for cyber threats.
- Phishing Attacks: Cybercriminals send deceptive emails or messages impersonating trusted entities, tricking VMAs into revealing sensitive information or downloading malware.
- Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs): Sophisticated, long-term cyber attacks involve persistent, targeted efforts to breach security defenses. APTs often leverage social engineering and advanced techniques for unauthorized data access.
- Supply Chain Vulnerabilities: Weaknesses in the interconnected supply chain, including software and hardware providers, can be exploited to compromise the integrity and security of healthcare technologies.
- AI-Related Threats: AI-based virtual assistants, like chatbots in healthcare, can pose cybersecurity threats by potentially mishandling sensitive patient data, leading to privacy breaches. Vulnerabilities in their algorithms may be exploited, allowing malicious actors to manipulate or influence healthcare decisions.
These threats underscore the need for robust cybersecurity measures to safeguard patient data, maintain the integrity of healthcare operations, and ensure the continued trust in VMAs.
How To Mitigate These Threats?
VMAs need secure remote access to battle the increasing cyber threats that they face. Secure remote access encompasses the array of security measures, policies, and technologies employed by organizations to provide secure network, device, and application access from locations outside the corporate office, ensuring a high level of security. In healthcare, its primary purpose is to protect sensitive patient data, healthcare records, Patient Health Information (PHI), Electronic Medical Records (EMR), and more.
Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA)
According to the Statistical Research Department, in 2022, almost 60% of respondents from the healthcare industry stated that their company has already implemented a zero-trust policy. Moreover, 29% of respondents mentioned that their company was planning to do so in six to 12 months. In the complex landscape of healthcare cybersecurity, adopting a Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) framework is crucial to mitigate threats faced by VMAs effectively. ZTNA operates on the principle of least privilege access, ensuring that only authorized users and devices can access healthcare networks and sensitive data. Several components of ZTNA play pivotal roles in bolstering the security posture of VMAs.
Here's how virtual medical assistants can ensure adherence to key GDPR principles:
- Identity and Access Management (IAM):, Implementing a robust IAM system is fundamental to ZTNA, ensuring that only authenticated and authorized individuals can access healthcare networks. By employing strong authentication methods like Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and passwordless entry through SSO, healthcare organizations and VMA staffing agencies can enhance user identity verification, mitigating the risk of unauthorized access to ePHI.
- Device Posture Check:, ZTNA incorporates a comprehensive Device Posture Check to evaluate the security health of devices seeking access. For VMAs, ensuring that devices comply with security policies, have updated software, and meet predefined security standards is imperative to ensuring that all non-compliant devices are restricted from accessing protected data.
- Monitoring and Reporting:, Continuous real-time monitoring is a cornerstone of ZTNA, providing visibility into user activities and potential security threats. Implementing robust monitoring and reporting mechanisms for VMAs allows prompt detection of anomalies or suspicious behavior. Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) tools can be employed to aggregate and analyze log data, facilitating timely threat response.
Site-to-Site VPN and Secure Remote Access:
A Site-to-Site VPN connects entire networks, enabling secure communication between separate physical locations, whereas a regular VPN typically connects individual devices to a remote server for secure access to the internet or a private network. Site-to-site VPN (Virtual Private Network) facilitates secure remote access for VMAs by establishing an encrypted connection between different physical locations. In healthcare, this technology allows virtual assistants located in, for example, a hospital and a remote data center to communicate securely over the internet by encrypting the data transmitted between these sites, protecting sensitive patient information from unauthorized access.
Meeting Global Regulatory Compliances:

VMAs must adhere to various compliance requirements to ensure the security and privacy of patient information. HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) is a fundamental standard that mandates strict controls. Virtual assistants need to implement robust encryption mechanisms to protect the confidentiality of patient data during storage, transmission, and access. Access controls must be in place, allowing only authorized personnel to interact with sensitive information. Regular audits and monitoring ensure ongoing compliance.
Additionally, VMAs must align with the HITECH (Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health) Act, which emphasizes the secure use of electronic health records (EHRs). This involves implementing measures like audit trails to track system activity and maintaining the integrity of electronic health information
Educating users and developers involved in virtual assistant operations is crucial. Training programs should emphasize the importance of compliance requirements for each global location, the proper handling of patient data, and the recognition of potential security threats. Periodic assessments and updates to security protocols ensure that virtual assistants evolve with changing compliance requirements and emerging cyber threats. By combining robust technical measures with comprehensive education programs, VMAs can meet global compliance standards, establishing a secure environment for handling sensitive patient information.
How PureDome Helps in Safeguarding Virtual Healthcare
HelloRache, a virtual healthcare services provider, faced security challenges in safeguarding sensitive medical data. By adopting PureDome's VPN solutions, they were able to address their cybersecurity concerns and ensure data privacy in the virtual healthcare industry. Read the complete case study here.
Conclusion
The rapid adoption of virtual medical assistants offers significant benefits for the healthcare industry, enhancing health outcomes and reducing costs. However, this growth exposes healthcare organizations to escalating cybersecurity threats, which furthers the need for robust security measures to be in place to protect patient data, uphold operational integrity, and maintain trust in the evolving realm of VMAs.
Stay up to date with the latest cybersecurity insights and best practices
Get the latest information, stories, and resources in your inbox. Subscribe for monthly updates.
Securing 1000+ Businesses Across The World.